Why Choose Us
About
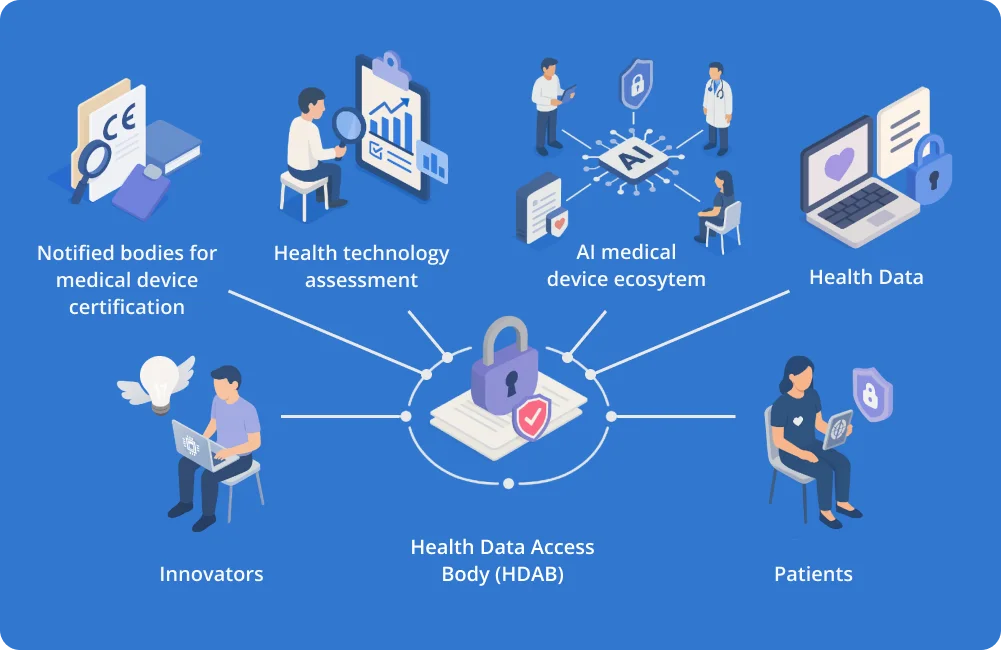
Supporting Health Data Access Bodies to establish AI pathways enabling Deployment of AI as medical device tools
The European Health Data Space (EHDS) regulation and the AI Act are set to transform the AI medical device ecosystem.
To harness the potential of these regulations and overcome existing bottlenecks, SHAIPED aims to optimize the pathways for AI medical device development, testing, and deployment by leveraging Health Data Access Bodies (HDABs).
SHAIPED will build on expertise from various EU-funded initiatives to identify tools and services to offer HDAB-supported pathways, for AI medical devices and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
SHAIPED will
The project will support the synergetic implementation of the EHDS regulation and the AI Act, strengthen the EHDS ecosystem and support capacity building at the HDAB level.
SHAIPED will also bring the EHDS ecosystem closer to the AI medical device innovation and regulatory ecosystems to accelerate the benefit generation of the new regulations. The project will contribute to ultimately reducing time-to-market for AI medical devices and enhancing the EU’s attractiveness and competitiveness in the field.
The project supports the Digital Europe program’s objective of bringing advanced digital technology to businesses, citizens, and public administrations.
In that context, SHAIPED aims at identifying, building new and strengthening existing pathways for AI medical device development, testing and deployment provided by Health Data Access Bodies. For that overall aim, SHAIPED leverages the unique positioning of HDABs while also involving other actors involved in the AI medical device product lifecycle and building on expertise and experience from other EU-funded initiatives
Demonstrate in practice how HDABs can bring added value to innovators who are developing, testing or deploying AI medical devices and
develop tools, pathways and methodologies that will enable HDABs to accelerate time to market for these devices and to improve patient outcomes.
Bring together different ecosystems to enhance the mutual understanding and build synergies around the EHDS and AI Act. These ecosystems include the EHDS ecosystem, AI medical device innovators and actors from the regulatory ecosystem like national competent authorities, HTA bodies, notified bodies under MDR/AI Act and others
Why Choose Us
Project Goals
SHAIPED’s overarching goals include the establishment of a streamlined, regulatory-aligned framework for AI medical devices, centered around the main goals.
Understand Existing Pathways and Identify Limitations
SHAIPED aims to evaluate the current pathways for AI medical device development and testing, identifying key limitations and bottlenecks that hinder their effectiveness. This involves mapping the regulatory landscape and clarifying roles within the lifecycle of AI medical devices.
Strengthen and Create Pathways Using EHDS and AI Act
By building on the regulatory frameworks set forth by the AI Act and the EHDS, SHAIPED aims to establish new and strengthen existing pathways, placing HDABs at the center. The goal here is to ensure HDABs can provide the necessary data support, ensuring data quality and privacy to facilitate the entire AI lifecycle for medical devices.
Build Capacity and Forge Connections Across Ecosystems
SHAIPED also focuses on strengthening the HDAB ecosystem by connecting it with various research, innovation, and regulatory communities, including innovators, notified bodies, health technology assessment (HTA) bodies, and other authorities. This creates a collaborative network that can better respond to regulatory demands and enables seamless integration within the EHDS ecosystem.
Real-World Testing of Pathways Through Use Cases
SHAIPED will conduct real-world testing of its established pathways by implementing use cases in critical areas. These use cases will provide insights into the operational challenges and benefits of HDAB-supported pathways, refining the support processes required for effective AI medical device deployment.
Reduce Time-to-Market and Enhance Patient Outcomes
Ultimately, SHAIPED aims to make the European market more attractive and competitive by reducing the time-to-market for AI medical devices and improving patient outcomes. By accelerating the integration of AI in healthcare, SHAIPED contributes to better healthcare delivery, timely patient care, and strengthened regulatory compliance.
Project Phases
SHAIPED is structured into three primary phases to effectively address the product life cycle of AI medical devices, adopting a phased approach to ensure comprehensive development and successful outcomes.
PHASE 1 – Months 1>9
Kick-off
Laying the Groundwork
PHASE 2 – Months 10>27
Design
Pathways Development and Use Case Realization
PHASE 3 – Months 28>36
Wrap-Up
Learning Consolidation & Recommendations
The first phase of SHAIPED focuses on establishing a foundational understanding of the current landscape and regulatory requirements for AI medical devices. During this initial phase, the project conducts an in-depth analysis of stakeholders, product life cycles, certification practices, and relevant legal frameworks. This groundwork provides essential insights into the existing ecosystem and lays the framework for the following project phases, ensuring that all stakeholders and regulatory aspects are well-aligned from the start.
Building on the insights from Phase 1, the Design phase centers on identifying specific opportunities for HDABs to impact AI integration in medical devices. This stage involves developing structured pathways and methodologies for HDABs to facilitate AI integration, leveraging HDAB tools and services to support AI medical device life cycles. The phase also includes the practical application of these pathways through the execution of real-world use cases, emphasizing the role of synthetic data and establishing protocols for data handling, compliance, and regulatory adherence.
The final phase focuses on consolidating the findings and outcomes from the previous phases. This includes finalizing methodologies, refining tools, and compiling learnings from the use cases to formulate guidelines and recommendations for future projects. By sharing these results and best practices, SHAIPED aims to foster widespread adoption of the developed frameworks across the AI healthcare ecosystem. Disseminating these insights not only facilitates knowledge transfer but also empowers stakeholders across Europe to integrate these AI pathways into their healthcare systems effectively.
Services
Project Phases
SHAIPED is structured into three primary phases to effectively address the product life cycle of AI medical devices, adopting a phased approach to ensure comprehensive development and successful outcomes.
Kick-off – Laying the Groundwork
The first phase of SHAIPED focuses on establishing a foundational understanding of the current landscape and regulatory requirements for AI medical devices. During this initial phase, the project conducts an in-depth analysis of stakeholders, product life cycles, certification practices, and relevant legal frameworks. This groundwork provides essential insights into the existing ecosystem and lays the framework for the following project phases, ensuring that all stakeholders and regulatory aspects are well-aligned from the start.
Design – Pathways Development and Use Case Realization
Building on the insights from Phase 1, the Design phase centers on identifying specific opportunities for HDABs to impact AI integration in medical devices. This stage involves developing structured pathways and methodologies for HDABs to facilitate AI integration, leveraging HDAB tools and services to support AI medical device life cycles. The phase also includes the practical application of these pathways through the execution of real-world use cases, emphasizing the role of synthetic data and establishing protocols for data handling, compliance, and regulatory adherence.
Wrap-Up – Learning Consolidation and Recommendations
The final phase focuses on consolidating the findings and outcomes from the previous phases. This includes finalizing methodologies, refining tools, and compiling learnings from the use cases to formulate guidelines and recommendations for future projects. By sharing these results and best practices, SHAIPED aims to foster widespread adoption of the developed frameworks across the AI healthcare ecosystem. Disseminating these insights not only facilitates knowledge transfer but also empowers stakeholders across Europe to integrate these AI pathways into their healthcare systems effectively.
Our Value
Work Packages
SHAIPED’s work is divided into structured work packages (WPs) focused on achieving key project objectives and milestones. These work packages ensure that SHAIPED’s goals are met through dedicated teams working on specific aspects of AI medical device deployment.
Our Value
Work Packages
SHAIPED’s work is divided into structured work packages (WPs) focused on achieving key project objectives and milestones. These work packages ensure that SHAIPED’s goals are met through dedicated teams working on specific aspects of AI medical device deployment.
Project Management and Coordination
Work Package 1, led by Health Data Hub (HDH), is responsible for overseeing SHAIPED’s project management and coordination. Running throughout the project’s entire timeline, WP1 ensures that all activities are effectively managed and that each partner’s contributions align with SHAIPED’s objectives. This includes organizing regular steering committee and consortium meetings to maintain project cohesion, address potential challenges, and align on progress. WP1 implements a comprehensive evaluation framework with defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track milestones and assess project outcomes. By setting up structured reporting and risk management protocols, this work package ensures transparency, accountability, and swift decision-making within the consortium. Additionally, WP1 is responsible for overseeing administrative and financial activities, ensuring that all partners meet compliance standards under the Consortium Agreement and Grant Agreement.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Work Package 2, led by the Croatian Institute of Public Health (CIPH), focuses on communication and stakeholder engagement to amplify SHAIPED’s visibility and impact. This work package is dedicated to promoting the project’s goals, milestones, and achievements to diverse audiences, including healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the public. WP2 develops a comprehensive communication plan that identifies target audiences, crafts key messages, and selects appropriate engagement channels to reach stakeholders effectively. In addition to developing SHAIPED’s visual identity, WP2 produces various outreach materials, including newsletters, press releases, and scientific publications, to build SHAIPED’s brand and increase awareness across Europe. WP2 also organizes events to encourage dialogue and collaboration, fostering a network of stakeholders committed to SHAIPED’s mission.
HDAB Mapping and Tools Development
WP3 brings the medical device ecosystem within the context of the EHDS, conceptualizing the AI as medical device product lifecycle, mapping HDAB tools, services and pathways incl. the study of synthetic data, and mappingthe regulatory backdrop.
Work Package 3, led by Sciensano (Belgium), focuses on identifying and mapping the tools, services, and resources required by Health Data Access Bodies (HDABs) to support the development and deployment of AI as medical devices. This work package is essential for creating a structured, well-defined pathway for AI medical device integration, leveraging synthetic data and addressing regulatory needs within the context of the EHDS. WP3 involves a comprehensive analysis of the AI medical device lifecycle, mapping HDAB-provided tools and services, and ensuring these resources align with legal and regulatory standards. This work also includes a study on the use of synthetic data to support data privacy while maintaining data utility.
AI Deployment Pathways
WP4 will focus on deployment pathways, diving deeper into latter phases of the AI medical device product lifecycle and investigating how real-world data and services provided by HDABs can contribute there.
Work Package 4, led by the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), focuses on creating robust deployment pathways for AI as medical devices, with a particular emphasis on real-world application. This work package delves into the latter stages of the AI medical device lifecycle, examining how real-world data (RWD) provided by HDABs can enhance the deployment and validation processes for AI solutions. WP4 develops a framework for deploying AI medical devices in clinical settings, accounting for regulatory requirements and operational challenges. By utilizing RWD, WP4 aims to refine deployment strategies, ensuring that AI tools can be integrated seamlessly within existing healthcare infrastructures. This work package addresses practical challenges in data management, compliance, and real-world effectiveness, ensuring that the deployment pathways align with both the EHDS and AI Act.
Pilot Project Implementation and Testing
WP5 will support three very concrete AI medical device testing and deployment projects to gain insights into the challenges and opportunities of HDAB support and real-world data usage. Through mature use cases, the project will test and refine established pathways, and support capacity building at HDAB level.
Work Package 5 is dedicated to testing and validating the HDAB-supported pathways for AI medical devices through real-world pilot projects. This work package takes SHAIPED’s theoretical frameworks and tools developed in previous work packages and applies them in three specific use cases across different healthcare settings. WP5 assesses the challenges and effectiveness of these deployment pathways in live environments, gathering insights into the practical application of HDAB resources. By focusing on diverse use cases WP5 aims to refine the HDAB pathways and tools, ensuring they meet real-world requirements and regulatory standards. This testing phase is critical for identifying improvement areas and ensuring that SHAIPED’s methods are feasible, effective, and scalable for widespread adoption across the EU.
Competitiveness And Benefits For The Society
Artificial Intelligence presents vast opportunities for healthcare systems to improve patients’s lives
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to be a key driver of technological advancement, revolutionizing various sectors and enhancing our quality of life. AI holds particular promise for health systems, which are under considerable strain. In healthcare, AI solutions are relatively mature, especially in areas such as imaging and decision support. These technologies can greatly alleviate the burden on healthcare systems, and improve patient outcomes. In the context of the European Health Data Space, it will be crucial to ensure that the organisational, legal and technical pathways for the (secondary) use of health data are in place so that innovators can move towards the deployment at scale.
This initiative will aim to reduce the barriers to entry for innovators within the EU market
To fully harness the potential of AI, it is essential to establish efficient pathways for its development, testing, and deployment. This is particularly crucial for the European Union (EU) to remain attractive to innovators seeking to develop, test, and deploy their solutions within its borders. Currently, the EU is often perceived as a more heavily regulated environment, which can discourage innovation. One of the significant barriers to AI development in the EU is access to data. Without ample data, the development of robust AI solutions is hindered. Another challenge lies in the certification process for medical devices, including software as medical devices (SaMD). Recently, innovators have shown a preference for markets like the United States and understanding the reasons behind that is a prerequisite to changing course. A more effective use of real-world data by clear pathways supported by Health Data Access Bodies could be an effective remedy.
Certification Process Comparison: Analyzing medical device certification timelines and processes across markets to determine potential HDAB roles.
Post-Market Surveillance: Leveraging HDAB-provided real-world data for post-market surveillance and clinical follow-up.
Performance Assessment: Using real-world data to evaluate AI medical device performance, informing HTA decisions.
This initiative will aim to ensure that European conditions (patient data, standards & regulations) are incorporated into the development process of AI medical devices.
To ensure the effectiveness of AI tools for EU patients and citizens, it is imperative to use EU-specific data for training AI algorithms. Utilizing local data ensures that AI solutions are tailored to the unique demographic and clinical characteristics of our population, leading to more accurate and relevant outcomes. By aligning AI innovations with the specific needs and regulatory frameworks of the European Union, we can maximize the benefits of these technologies for our citizens. This initiative will aim to ensure that AI technologies deliver benefits that extend beyond corporate interests to significantly enhance societal well-being.
This initiative places a strong emphasis on managing the risks associated with AI deployment, ensuring that these technologies are safe, ethical, and beneficial for all segments of society.
The project builds on the robust framework provided by the AI Act and European Health Data Space Regulation as well as other relevant EU regulations, including the Medical Device Regulation as well as the HTA regulation. The project will develop pathways and strengthen capacities throughout the EU that will encourage AI development, testing and deployment. Thereby the project will contribute to 1) competitiveness gains and 2) improved patient outcomes. The project will also support the implementation process of the EHDS regulation and the AI act and thereby have positive co-benefits for health innovation and research beyond the AI pathways.
Expected Outcomes And Deliverables
Report on AI Testing and Deployment Pathways: Limitations and Gaps in the Current Landscape
Report on the identified pathways for testing and deployment of AI in health and their limitations and gaps in the current landscape: This goal will be fulfilled with WP3 “Tools and services for AI development, test and deployment pathways in the EHDS” that will conduct a robust landscape analysis of the AI medical devices lifecycle and identify relevant tools and services to establish pathways. ( notably through tasks 3.1 and 3.2 (full details below)). This work package will produce the following deliverable “D3.1 – Guidelines for HDABs to support AI development” that allow to identify pathways for testing and deployment of AI in health and their limitations and gaps in the current landscape.
Pathways for AI in Healthcare: Role of HDABs, TEFs, and EDIHs Under EHDS and AIA
Description of pathways based on health data access bodies’ services and other key actors such as TEFs and EDIHs, where relevant, in light of the EHDS and the AIA: This objective will be met jointly by WP 3 and WP 4, with support from WP2. Work package 3 will analyze the different points at which HDAB like structures will be able to impact the lifecycle of AI medical devices, drawing concrete descriptions of pathways mapping current HDAB capacities and previous European projects that can contribute.
WP3 will also produce “D3.3 – Regulatory backdrop of AI medical device development, testing and deployment within the EHDS2 ecosystem” providing the regulatory background of the pathways based on EHDS and AIA. Moreover, work package 4, will provide a focus on deployment pathways through the establishment of new pathways for market access and certification, post market surveillance and post market clinical follow-up and Heath Technology Assessment (HTA) and decision making for reimbursement and financing. WP2 will engage with key stakeholders in order to test and validate the pathways.
Guidelines for HDAB Capabilities: Supporting AI Development, Testing, and Deployment
Guidelines for creating and deploying the necessary capabilities for HDABs to support the development, testing and deployment pathways for AI in healthcare: This goal will be met with WP 3 and more specifically task 3.2 “HDAB tools and services mapping” and deliverable D3.1 “Guidelines for HDABs to support AI development”. WP5 with the use cases wil also contribute to building capacity at HDAB level.
Evaluation of AI Use Cases: Reports on Tests and Real-World Showcases
Reports on the tests and showcases conducted: In the project proposal, a strong focus will be given to the realizationof use cases, outlined in work package 5, that will both benefit from the expertise of the two first work packages (WP3 and WP4) but also feed these previous WPs with real-world learnings of concrete applications. This WP will culminate in the production of use case learnings.
Recommendations for AI Pathway Implementation: EHDS Opportunities and AIA Compliance
Recommendations for the implementing of development, testing and deployment pathways of AI in health based on the opportunities offered by the EHDS and the requirements of the AIA: This goal will be met with task 3.4 “Regulatory backdrop of AI medical device development, testing and deployment within the EHDS2 ecosystem. “ and deliverable D3.3 “Regulatory backdrop ofAI medical device development, testing and deployment within the EHDS2 ecosystem ” among WP3. In addition work package 4 will provide recommendations for improved EU market access & certification of AIasMD solutions through deliverable D4.1.
Long Term Policy Objectives, Policies and Strategies Contribution
SHAIPED supports the European Data Strategy by advancing the European Health Data Space and facilitating AI Act implementation, driving innovation in AI medical devices.
1. Interplay Between the AI Act and EHDS: Legal and Regulatory Assessment for AI in Healthcare
This project will carry out a comprehensive assessment of the interrelationship between AI Act and EHDS, eg. Investigating how the Health Data Access Bodies established under the EHDS regulation can fulfill their role with regards to AI development. SHAIPED will explore how AI pathways can support AI medical devices in their lifecycle, given requirements from the AI Act, medical device regulation and HTA regulation, among others. It will also provide some practical feedback on legal and regulatory issues encountered in the different tasks and use cases.
2. Accelerating AI Medical Device Market Entry: Overcoming Certification and Data Challenges
The project aims to accelerate the market entry of AI medical devices by identifying HDAB-level services that support AI development, testing, and deployment. It addresses EU market challenges, such as certification practices and limited guidelines, and explores how real-world data can enhance decision-making by HTA bodies. Key areas of investigation include
Certification Process Comparison: Analyzing medical device certification timelines and processes across markets to determine potential HDAB roles.
Post-Market Surveillance: Leveraging HDAB-provided real-world data for post-market surveillance and clinical follow-up.
Performance Assessment: Using real-world data to evaluate AI medical device performance, informing HTA decisions.
3. Enhancing EHDS Maturity for AI: Building HDAB Capabilities and Ecosystem Integration
The project will address the varying maturity levels of the EHDS ecosystem in supporting AI medical device development, testing, and deployment. While some HDABs are not yet established, others lack experience with AI projects. The project will outline required capabilities, map existing capacities, and propose solutions such as synthetic data creation to showcase HDAB potential. It will also support capacity building for HDABs to enhance their services and tools. By doing so, the project will create links between the EHDS ecosystem and EU-supported actors like Testing and Experimentation Facilities, European Digital Innovation Hubs, data holders and innovators.